
Microscope diagram Tom Butler Technical Drawing and Illustration Projects Pinterest
Microscope Parts Labeled: Parts of A Microscope 1. Eyepiece Lens and Eyepiece Tube 2. Objective Lens 3. Tube 4. Base 5.

Parts of a microscope with functions and labeled diagram
Activity 1: Parts of a Microscope. A microscope magnifies the image of an object through a series of lenses. The condenser lens focuses the light from the microscope's lamp onto the specimen. The light then passes through the object and is refracted by the objective lens. The objective lens is the more powerful lens of a microscope and is.
Parts of a Compound Microscope — Learning in Hand with Tony Vincent
In this activity, students identify and label the main parts of a microscope and describe their function. By the end of this activity, students should be able to: identify the main parts of a microscope. describe the function of the different parts of a microscope. Download the Word file (see link below) for: background information for teachers.

Clipart microscope parts labeled WikiClipArt
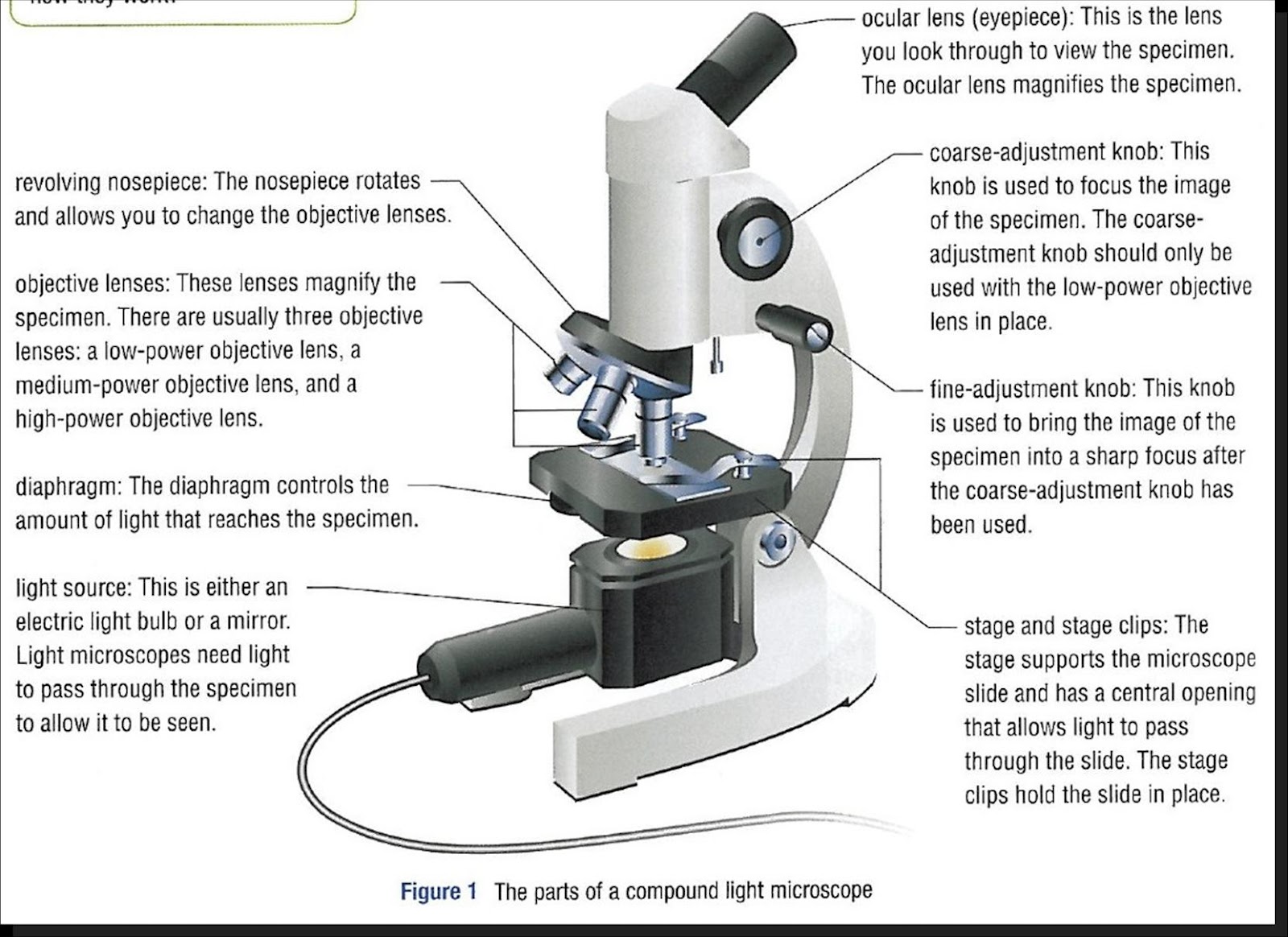
Eyepiece lens magnifies the image of the specimen. This part is also known as ocular. Most school microscopes have an eyepiece with 10X magnification. 2. Eyepiece Tube or Body Tube. The tube hold the eyepiece. 3. Nosepiece. Nosepiece holds the objective lenses and is sometimes called a revolving turret.

Proper Use & Care of Microscopes Clinician's Brief
This activity has been designed for use in homes and schools. Each microscope layout (both blank and the version with answers) are available as PDF downloads. You can view a more in-depth review of each part of the microscope here. Download the Label the Parts of the Microscope PDF printable version here.
Parts of a Microscope Labeling Activity
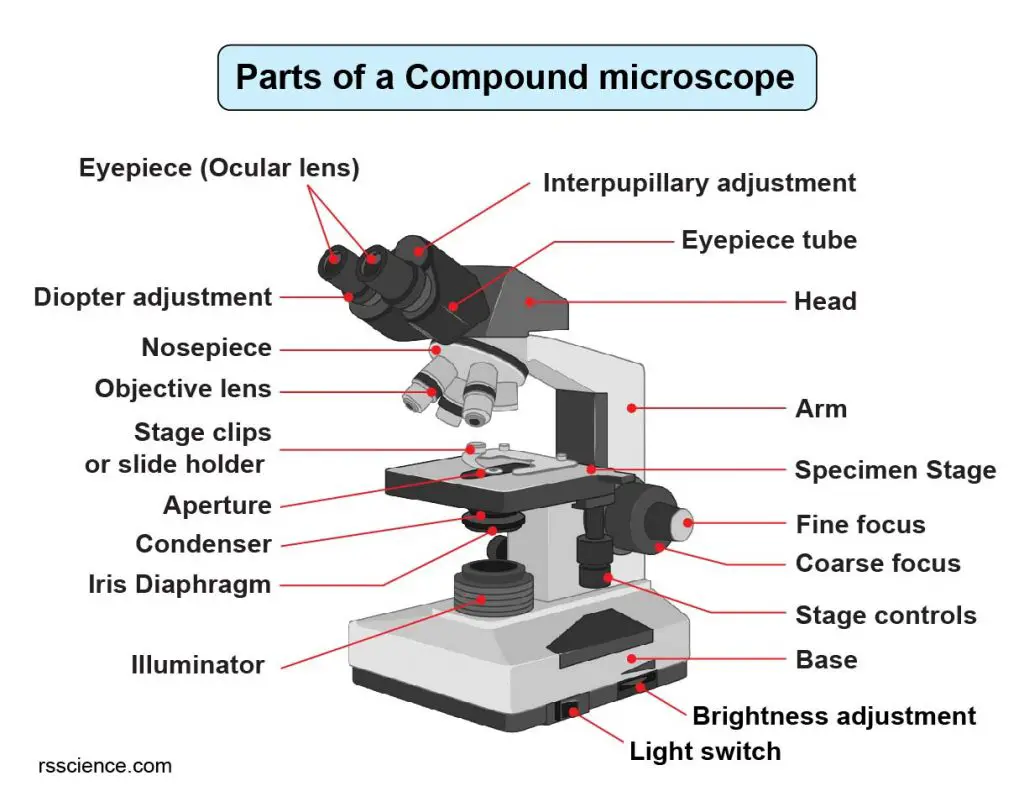
Parts Of a microscope. The main parts of a microscope that are easy to identify include: Head: The upper part of the microscope that houses the optical elements of the unit.; Base: The base is attached to a frame (arm) that is connected to the head of the device.The base of the microscope provides stability to the device and allows the user's hands to be free to manipulate other aspects of.
Parts Parts And Functions Of A Microscope
Structure of a cell > Introduction to cells Microscopy Google Classroom Introduction to microscopes and how they work. Covers brightfield microscopy, fluorescence microscopy, and electron microscopy. Introduction

Parts of a Microscope The Comprehensive Guide Microscope and Laboratory Equipment Reviews
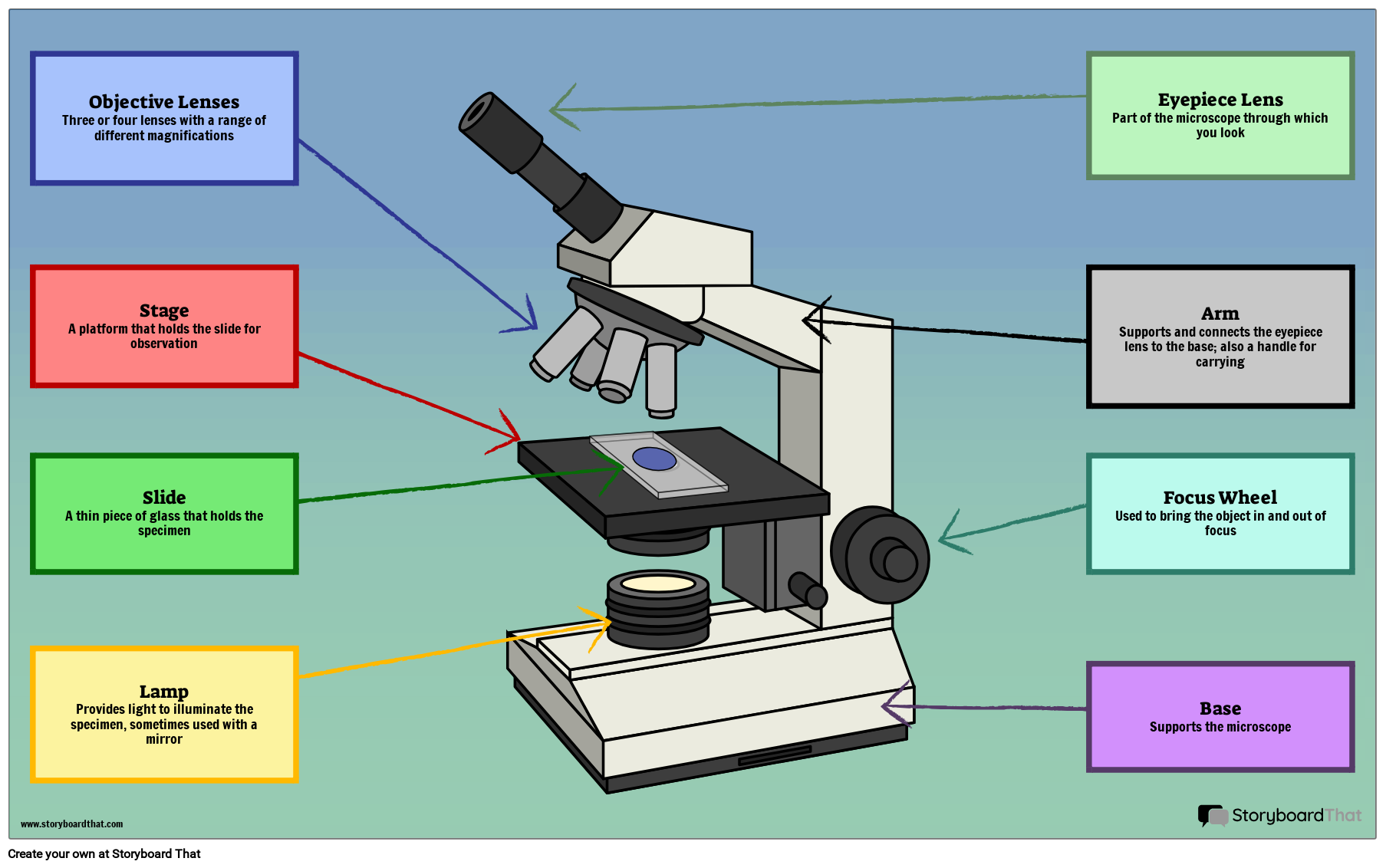
a. Mechanical Parts of a Compound Microscope Foot or Base Pillar Arm Stage Inclination Joint Clips Diaphragm Nose piece/Revolving Nosepiece/Turret Body Tube Adjustment Knobs b. Optical Parts of a Compound Microscope Eyepiece lens or Ocular Mirror Objective Lenses
1.5 Microscopy Biology LibreTexts
Do you know? Antoni van Leeuwenhoek is the first person to see bacteria. There are different types of microscopes based on their working mechanism and functions, but the microscopes can be broadly classified into; Light (optical) microscope and Electron microscope Table of Contents The Light Microscope Parts of Compound Microscope
Compound Microscope Parts Labeled Diagram and their Functions Rs' Science
Which part of the microscope do you look through to see a specimen? the eyepiece (also called the ocular lens) How do the focusing knobs help us as we use a microscope? They help move the stage up/down and bring the specimen into focus so it can be observed in detail.
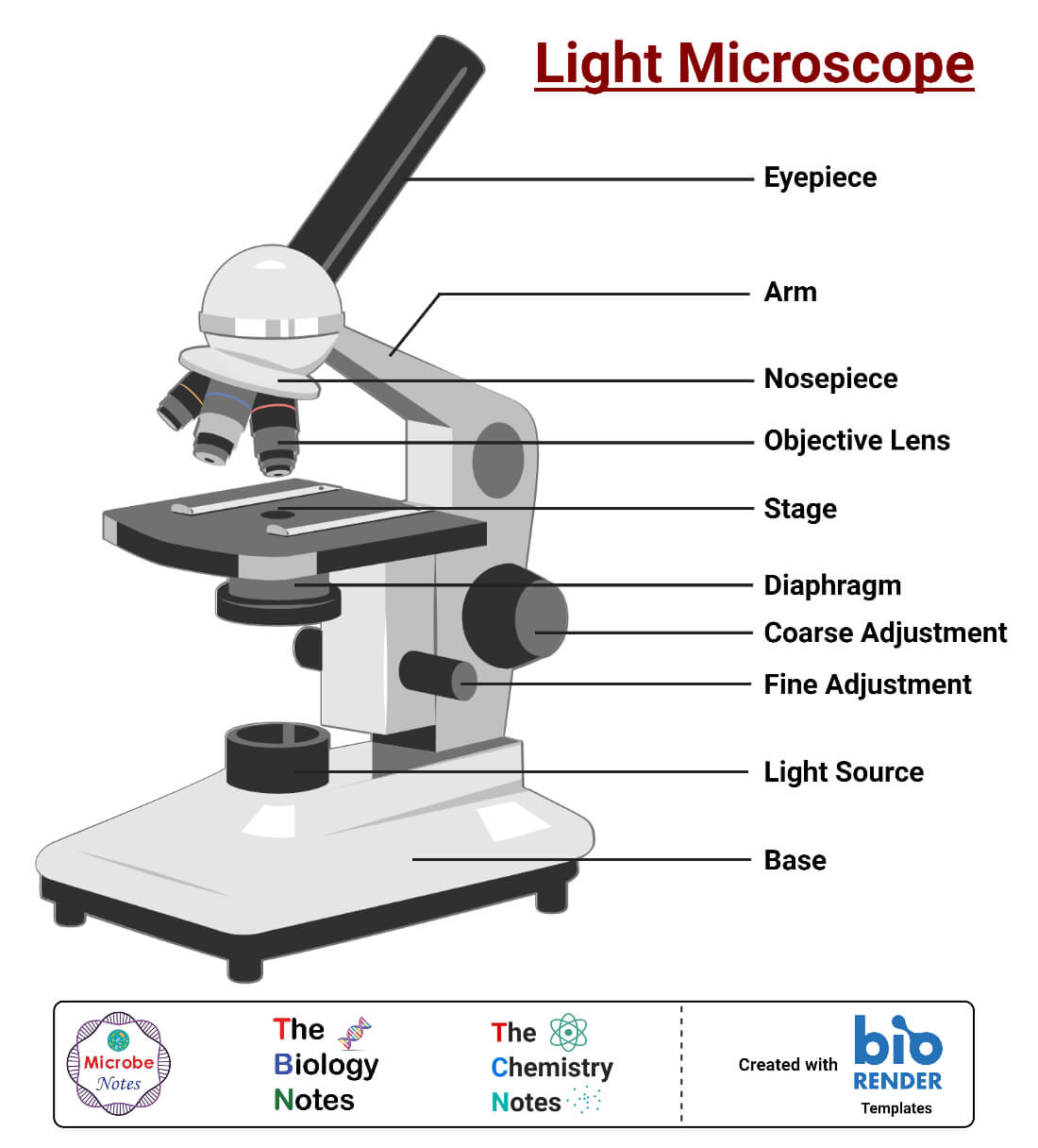
Light Microscope Definition, Principle, Types, Parts, Labeled Diagram, Magnification
There are 1000 millimeters (mm) in one meter. 1 mm = 10 -3 meter. There are 1000 micrometers (microns, or µm) in one millimeter. 1 µm = 10 -6 meter. There are 1000 nanometers in one micrometer. 1 nm = 10 -9 meter. Figure 1: Resolving Power of Microscopes. The microscope is one of the microbiologist's greatest tools.

Microscope Diagram Labeled, Unlabeled and Blank Parts of a Microscope
Parts of the Microscope with Labeling (also Free Printouts) A microscope is one of the invaluable tools in the laboratory setting. It is used to observe things that cannot be seen by the naked eye. Table of Contents 1. Eyepiece 2. Body tube/Head 3. Turret/Nose piece 4. Objective lenses 5. Knobs (fine and coarse) 6. Stage and stage clips 7. Aperture
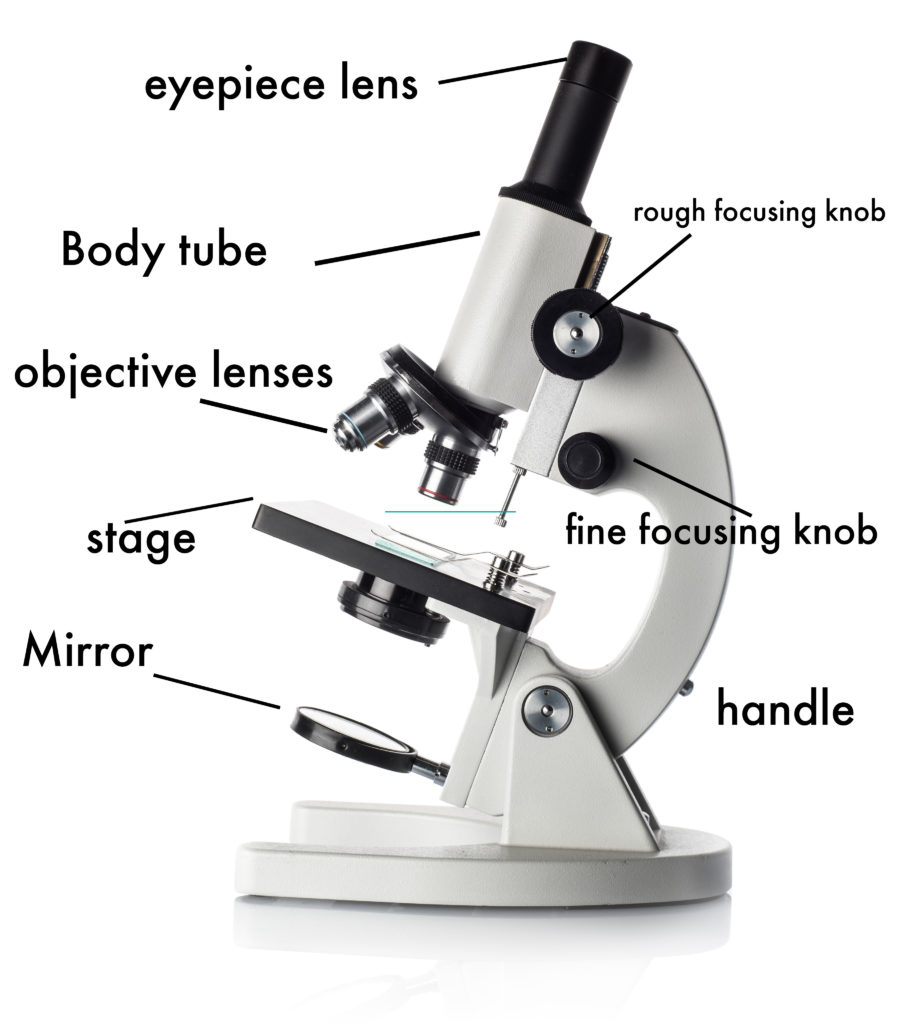
How to Use a Microscope
Having been constructed in the 16th Century, microscopes have revolutionized science with their ability to magnify small objects such as microbial cells, producing images with definitive structures that are identifiable and characterizable. Derived from Greek words "mikrós" meaning "small" and "skópéō" meaning "look at". Table of Contents

Parts of a Microscope and their function
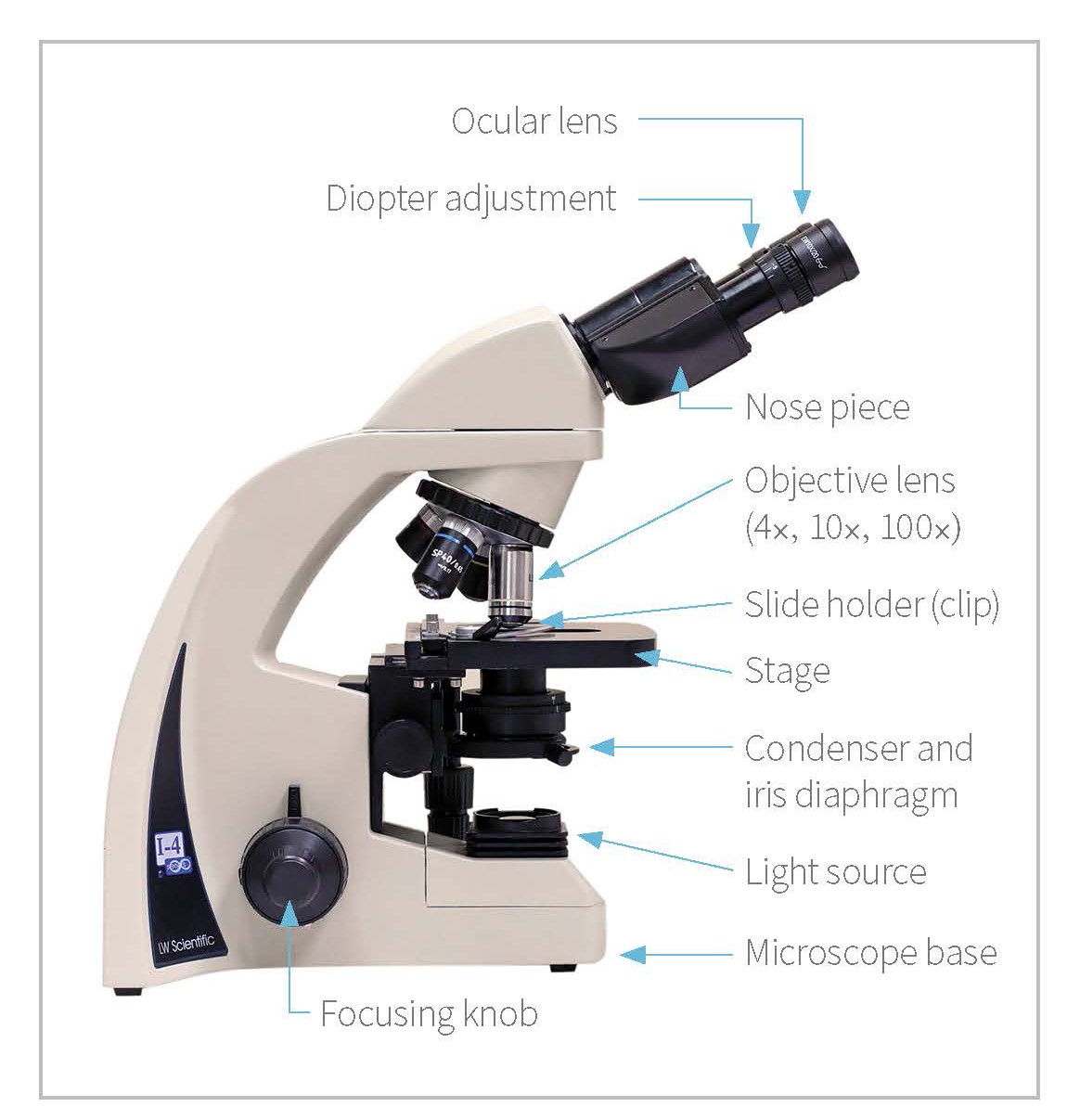
Parts of a Compound Microscope Here are the important compound microscope parts. Eyepiece: The lens the viewer looks through to see the specimen. The eyepiece usually contains a 10X or 15X power lens. Diopter Adjustment: Useful as a means to change focus on one eyepiece so as to correct for any difference in vision between your two eyes.
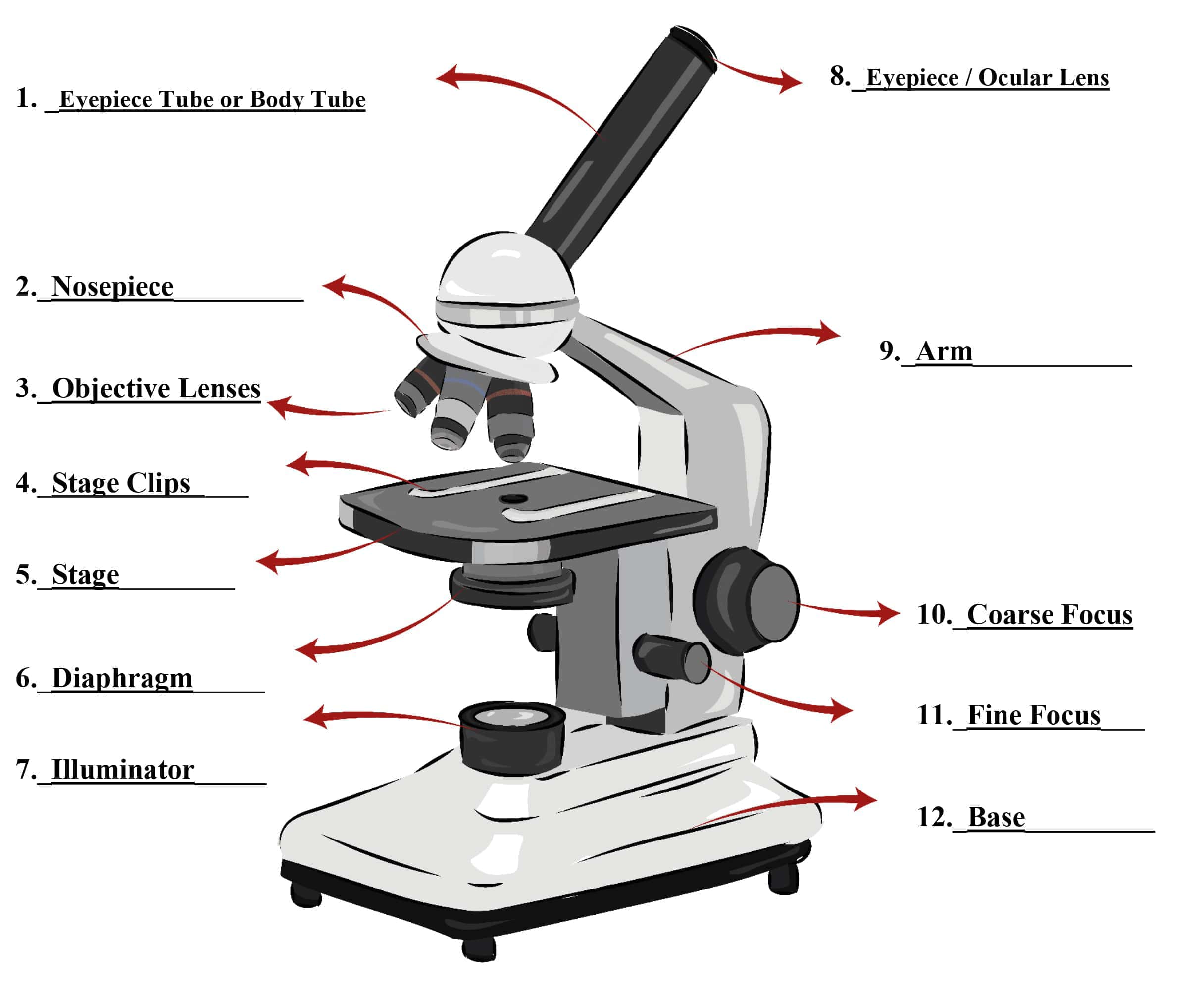
Parts of a Microscope SmartSchool Systems
Labeled parts of a microscope. General Rules. Always START and END with the low power lens when putting on OR taking away a slide. Never turn the nose piece by the objective lens. Do not get any portion of the microscope wet - especially the stage and objective lenses.
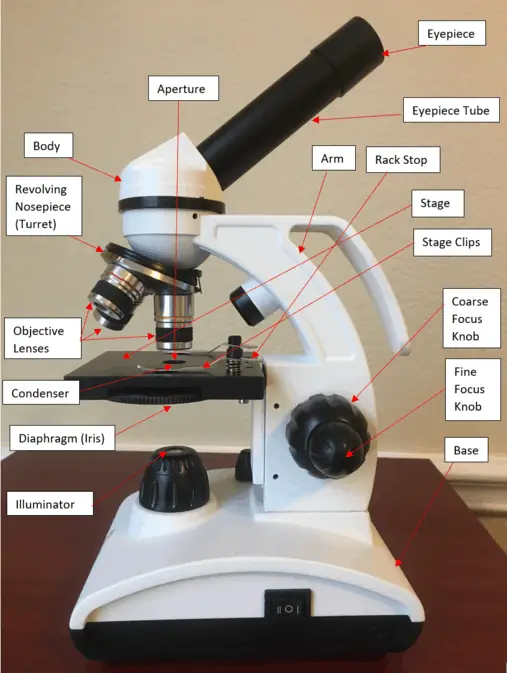
16 Parts of a Compound Microscope Diagrams and Video Microscope Clarity
Create a poster that labels the parts of a microscope and includes descriptions of what each part does. Click "Start Assignment". Use a landscape poster layout (large or small). Search for a diagram of a microscope. Using arrows and textables label each part of the microscope and describe its function. More options.